CV vs Resume: Your Foolproof Guide to Knowing When to Use Which
You have probably encountered the terms “CV (curriculum vitae)” and “resume” during your job hunt. Have you ever wondered if a CV and a resume are different from each other? In this article, JobStreet will help you impress potential employers with the most appropriate application document. But before anything else, you must learn the difference between a CV and a resume.
Importance of knowing the difference between a CV and a resume
Whenever you apply for a job, you must prepare a document that best introduces yourself to your potential employer. This document, either a CV or a resume, will play a key role in their decision-making process. Remember that you are in a competitive job market, and hirers will only have their eyes on the most compelling applications they receive.
Jobseekers often overlook the difference between a CV and a resume. Because of this, many applicants make the common mistake of sending whatever they have when a job opportunity arrives. However, if you submit the wrong document, hirers may disqualify you from the application process.
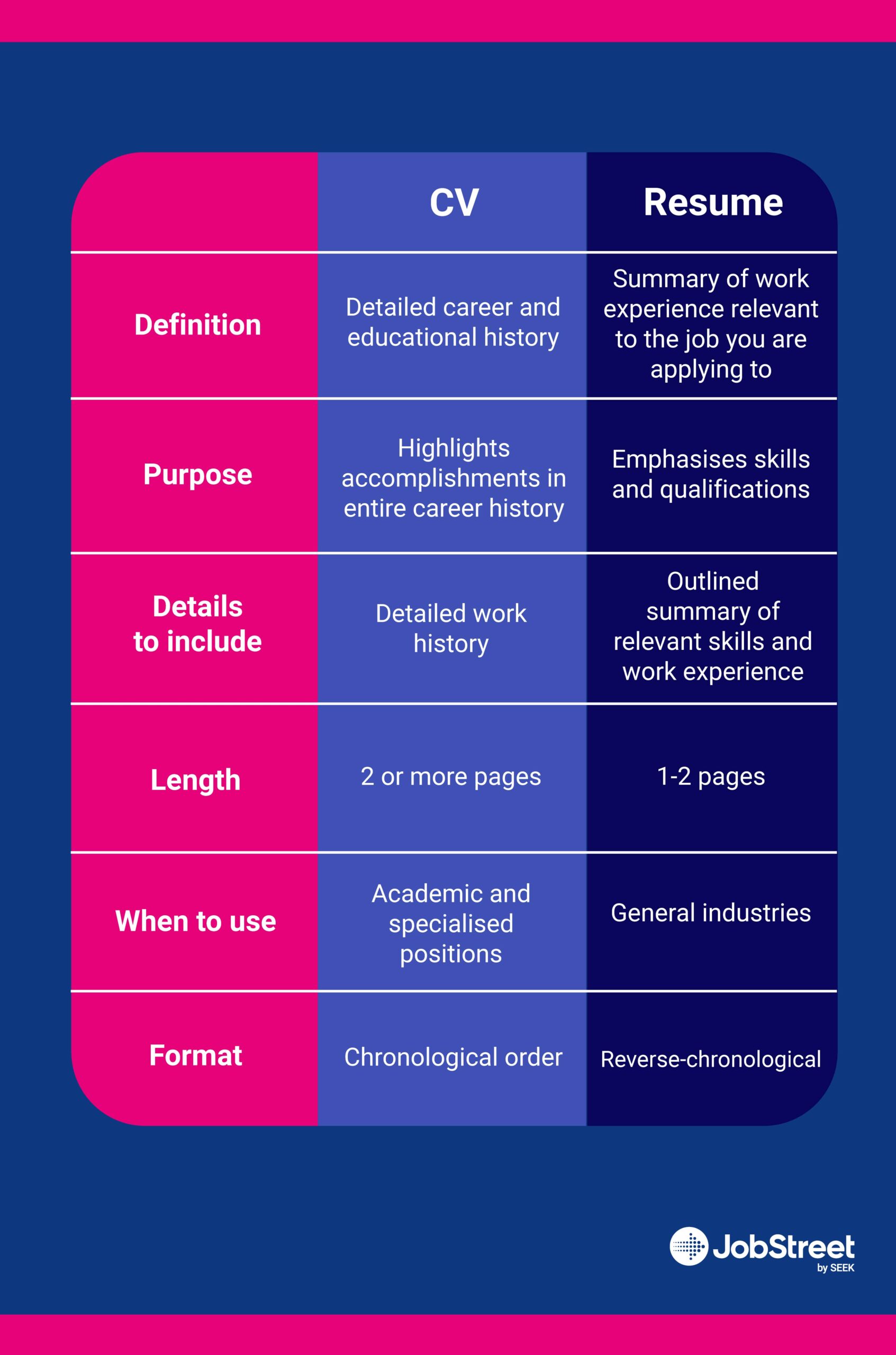
CVs and resumes share the common purpose of marketing jobseekers as desirable employees to potential employers. While some Southeast Asian countries tend to interchange the two terms, there are differences between a CV and a resume. Understanding the distinction can help propel you through the job application process.
What is a resume?
Definition
Your resume is an essential tool to get your job hunt started. Its name comes from the French word “résumé”, which translates to “summary” or “abstract”. This document outlines your relevant qualifications and experience required for the specific job.
Purpose
Employers use resumes to identify which candidates possess the skills and qualifications of their organisation. Your resume serves as your main marketing tool that will possibly land you the career you are eyeing. It showcases how your different skills can be helpful for the position you are applying to.
When to use
Resumes are typically used in Western countries like the US and Canada and some countries in Asia. They are commonly required in getting jobs in different organisations such as corporate, non-government, and non-academic. If you are applying for a job abroad, it is best to check with your potential employer what information they need or which document they require.
Details and length
Resumes come in different formats and templates, some with variations for particular professions. It is best to tailor your resume to the job you are applying for. Doing so can boost your chances of grabbing the attention of hirers. You can also consider the relevant keywords your target industry uses.
Keep a resume as short and strategic as possible, with a maximum of two pages. You do not have to include information about your entire career; instead, focus only on information suitable to the job you are applying to. If you are a fresh graduate, you can also include related internships or personal projects.
(Read more: 10 Resume Writing Tips for Jobseekers With No Work Experience )
A stellar resume should include the following information:
Contact details
Include your full name, mobile number, and email address. Some jobseekers add their current address for geographical advantages. If applicable to the position, you can also have your social media profiles or a link to your portfolio.
Introduction
Your introduction can be in the form of a resume summary or objective. It should give your potential employer a concise overview of your professional background and key qualifications.
Education
Highlight your school, highest degree earned, and relevant coursework. You can also add your GPA if the job description requires it.
Experience
List your relevant work experience in reverse-chronological order, starting with your most current job. Include your role, the name of the company, the years you worked there, your key responsibilities, and your notable successes. Remember also to include relevant accomplishments and certifications on your resume.
Skills
You should have a dedicated skills section where you can showcase your skills that are applicable to the position. Make sure to use a mix of hard and soft skills to demonstrate that you are a well-rounded candidate.
Format
There are several resume formats. Each format can be tailored for a specific job opening. The most common resume formats used are the following:
Chronological resume
Use this most common resume format by listing your work experience in reverse-chronological order, starting with your most recent position.
Functional resume
Focus on your skills and strengths rather than your work experience. By highlighting these, you can emphasise how qualified you are for the position. If you have gaps in your work history or have limited work experience, this is the format you can use.
Targeted resume
Carefully construct your work experience, skills, and education sections to emphasise the job requirements using exact keyword matching from the description. A targeted resume is beneficial when applying online, as it helps you rank higher in the applicant tracking systems used by employers.
Combination resume
This resume format highlights your skills and experience before listing your employment history in descending chronological order. It blends the functional and chronological resume formats. If you are making a distinct career change, you can consider this format.
(Read more: Resume Writing Tips: Which Resume Format Should You Use? )
What is a CV (curriculum vitae)?
Definition
The word “curriculum vitae” is a Latin term which translates to “course of one’s life”. A CV is commonly a multiple-page document that provides detailed information about your work experience, education, and achievements.
Purpose
A CV works like a career biography, where you showcase your passion and purpose for choosing a specific career path. It should give your potential employer a clear understanding of your growth as a potential employee. Your CV must communicate why the particular job you are applying for is the logical result of your career path.
When to use
CVs are commonly used for public service positions or teaching positions. It is ideal for specialised job roles that require specific expertise. Most European countries require their jobseekers to provide a CV.
Note:In some countries, CVs are synonymous with resumes. It is best to carefully read through the application instructions to know which document is required to apply.
Details and length
One difference between a CV and a resume is their length. Since CVs provide more details, they usually are lengthier than resumes. They should consist of the following:
Personal details
CVs provide in-depth information about jobseekers. Aside from your contact details, you can include your marital status, gender, date of birth, government-issued identification number, and nationality.
Career Summary
Your career summary must include a clear overview of your work history and career goals. Emphasise your responsibilities and accomplishments.
Academic history
Besides listing your education details, indicate the subjects you took, awards and honours you received, and further learning you enrolled in.
Work history
Unlike resumes, where you list down relevant experience, CVs require you to include your complete work history. They must provide your potential employer with a clear understanding of how you got into your current career path and where you are headed.
Skills
You can include different skill sets in a CV. This may be in language skills and other interests you are currently developing.
Published work
Include papers you wrote or co-wrote, like your thesis topic. If you presented during conferences, you could include them in this section.
Certifications and memberships
This section in a CV pertains to specialised fields, like engineering or accounting, where employers would require candidates to be members of specific professional bodies.
Format
CVs present your work experience in a structured and chronological format. Your CV grows over time as more experience and achievements are added. Different organisations, industries, and countries may require various styles and information.
Quick summary
Understanding the difference between a CV and a resume can be confusing at first. However, by carefully putting together your documents, you can create what is best suited to your job application and make an excellent first impression. Make sure you have both in hand, so you can present them when an opportunity arrives.
#LetsGetToWork and start your job seeking journey today! Don’t forget to update your JobStreet profile to get the latest notifications of your career choice. You can also download the JobStreet app in the Google Play Store or the App Store to easily access the latest job postings.
Visit the Career Resources Hub for more tips and career advice.